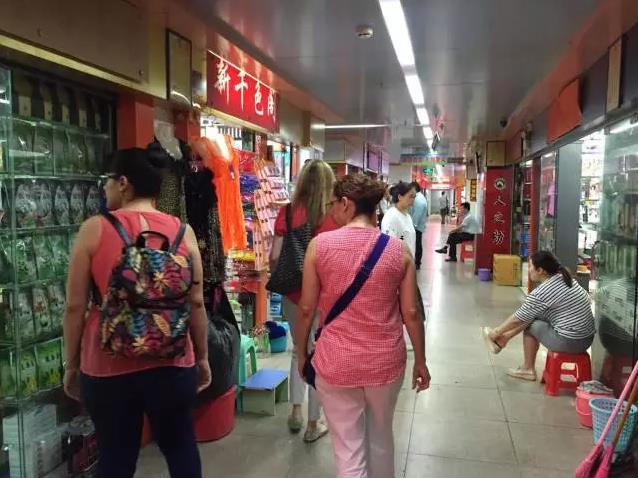
Typhoid fever is a common bacterial diseases which is transmitted by contaminated water or food of infected person by salmonella enterica bacteria.The disease has received various names, such as gastric fever, nervous fever, enteric fever, abdominal typhus, infantile remittant fever, slow fever, and pythogenic fever. The meaning of typhoid is resembling typhus and it comes from the neuropsychiatric sypmtoms common to typhoid and typhus.
Signs and Symptoms
Typhoid fever is divided to four stages and each stages are approximately one week.
In the first week, temperature rises slowly, fever fluctuations are seen with relative bradycardia, malaise, headache, and cough. In quarter of cases had epistaxsis, and abdominal pain is also possible.it seen decreasing in the number of circulation white blood cells with eosinopenia and lyphocytosis, also blood cultures are positive for salmonella typhi or parathypi. The widal test is negative in first week which is we use for discover salmonella bacteria in patient.
In the second week of infection, patient lies flat with high fever around 40 °C with bradycardia, classically with a dicrotic pulse wave. Delirium is frequent, often calm, but sometimes agitated. This delirium gives to typhoid the nickname of “nerveous fever”. Rose spots appear on the lower chest and abdomen in around a third of patients. There are rhonci in lung bases. The abdomen is distended and painful in the right lower quadrant, where borborygmi can be heard. Diarrhea can occur in this stage: six to eight stools in a day, green, comparable to pea soup, with a characteristic smell. However, constipation is also frequent. The spleen and liver are enlarged and tender, and there is elevation of liver transaminases. The widal test is stongly positive , with antiO and antiH antibodies. Blood cultures are sometimes still positive at this stage. The major symptom of this fever is that the fever usually rises in the afternoon up to the first and second week.
In the third week of typhoid fever, a number of complications can occur: Intestinal haemorrhage due to bleeding in congested Peyer’s patches; very serious but is usually not fatal. Intestinal perforation in the distal ileum: this is a very serious complication and is frequently fatal, itmay occur without alarming symptoms until septicaemia or diffuse peritonitis sets in. Encephalitis. Neruropsychiatric symptoms with picking at bedclothes or imaginary objects. Metastatic abscesses, cholecystitis, endocarditis and osteitis. The fever is still very high and oscillates very little over 24 hours. Dehydration ensues, and the patient is delirous. One third of affected individuals develop a macular rash on the trunk.Plateler count goes down slowly and risk of bleeding rises. By the end of third week, the fever starts subsiding. This carries on into the fourth and final week.
Transmission
The bacterium that causes typhoid fever may be spread through poor hygiene habits and public sanitation conditions, and sometimes also by flying insects feeding of feces. Public education campaigns encouraging people to wash their hands after defecating and before handling food are an importan component in controlling spread of the disease.
Prevention
Sanitation and hygiene are the critical measures that [...]
The post Typhoid fever appeared first on Medicinase.